Clare Oxborrow06 Jan 2022
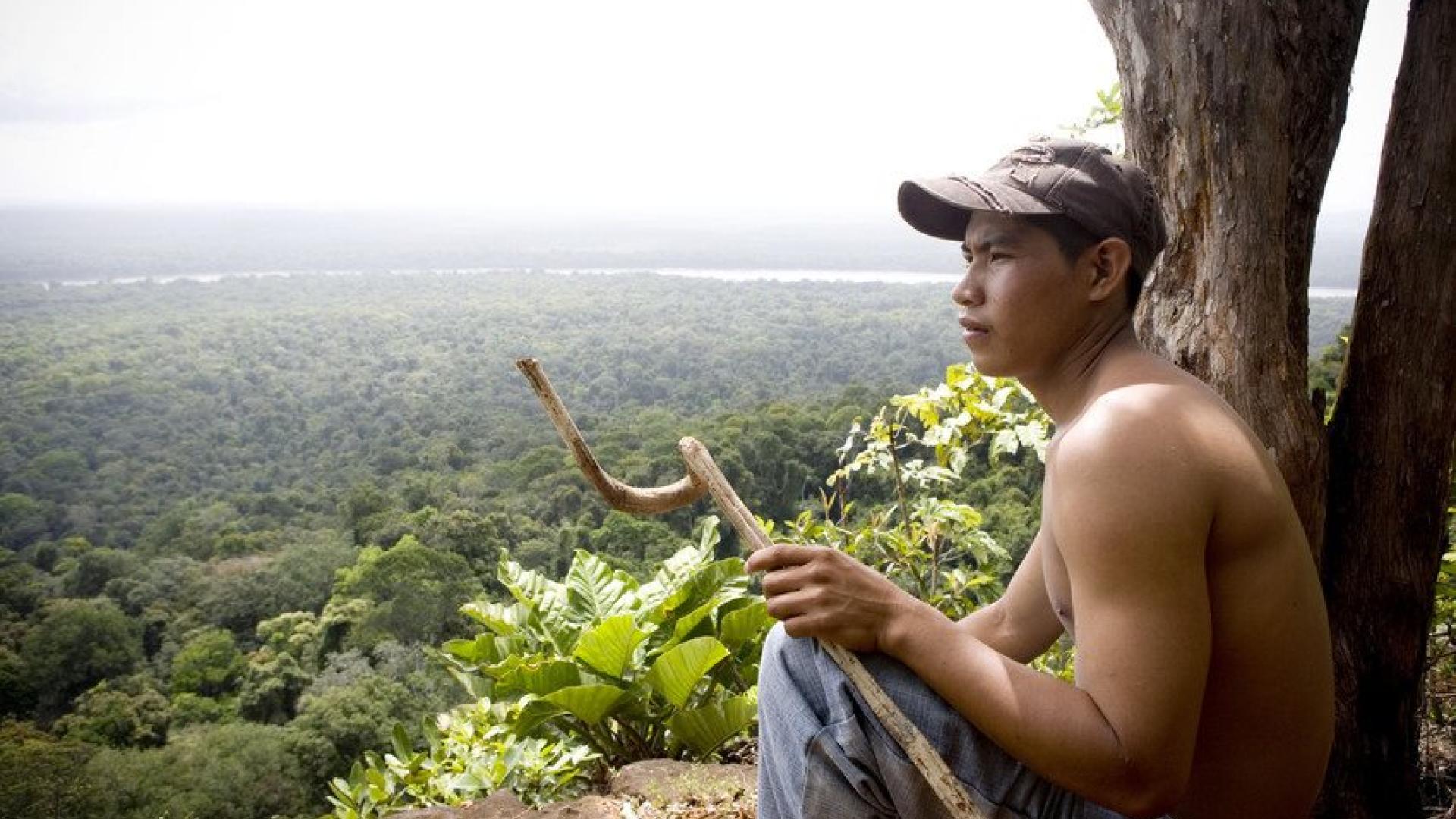
Thirteen years ago, standing near a field of soybeans in Paraguay, I could feel my eyes stinging and my throat burning from the herbicides sprayed onto the crops. Although unpleasant, it was nothing compared to what the indigenous Guarani communities experienced every day – surrounded by vast fields of soy monocultures, living with incessant chemical spraying and suffering contaminated water that damaged their health.
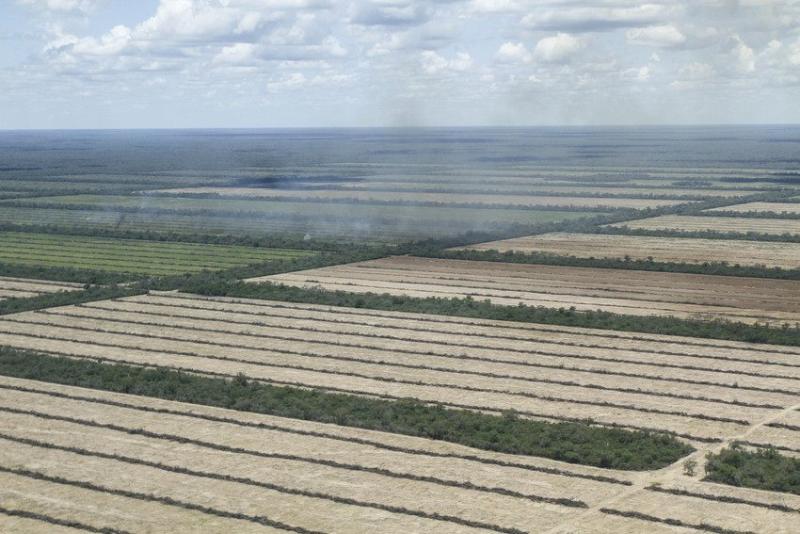
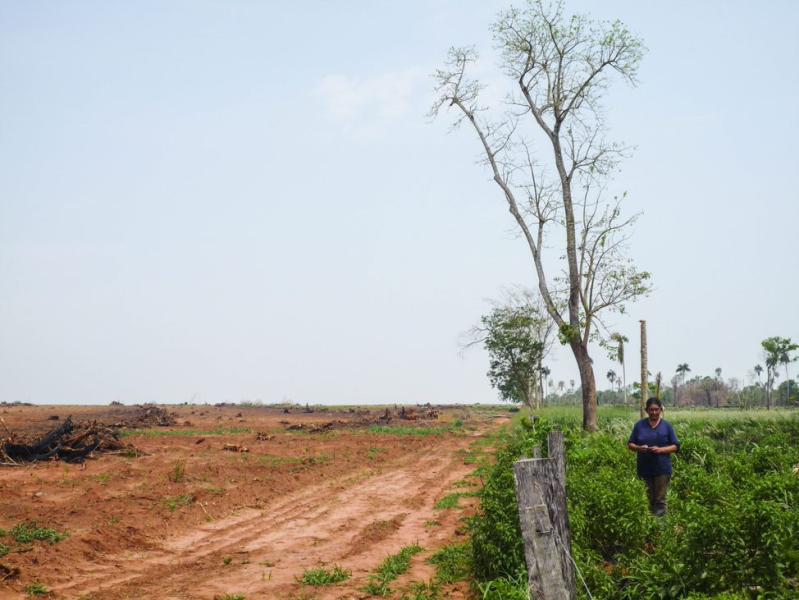
They had witnessed the destruction of Atlantic forest and tropical savannah (Cerrado), what was once a thriving environment with small-scale food production was now reduced to a sterile monoculture by the agribusiness giants producing animal feed. All to satisfy Europe's insatiable appetite for pigs and chickens.
Sadly, this experience could be replicated in many countries around the world where forests are cleared for intensive agriculture to grow commodities for the Global North like soy, palm oil, cocoa, coffee and rubber.
Even more shocking, the most vulnerable communities already affected by climate breakdown and loss of sustaining ecosystems are also subject to violence, intimidation and even death.
Hold corporations to account
Powerful companies control commodity supply chains and facilitate demand for meat, timber and cheap food and fuel by consumers in the Global North and emerging economies, at the expense of the planet and people. We need governance measures to rein in the companies behind much of this devastation.
The UK government has recognised that our demand for cheap commodities drives forest destruction and the new Environment Act contains provisions to address deforestation. While it's encouraging to see a requirement for some businesses to conduct due diligence to ensure their supply chains are free of products that come from illegally deforested areas, it doesn't go far enough. It fails to address human rights and won’t protect indigenous communities (more on this below).
Former UK prime minister Boris Johnson stated that dealing with climate change and biodiversity loss would be the government’s number one international priority this decade – and rightly so. But taking action on these issues must include addressing the impacts on people. The destruction of nature and the impact of global warming are inextricably linked to environmental justice with often devastating impacts on local communities.
If the UK is serious about addressing the nature crisis alongside the climate emergency, it must make it a legal duty for corporates, including the giant retailers, to eliminate deforestation and protect local communities from harm.
Why is this happening?
Demand for commodities drives deforestation
Trade and the consumption of commodities have become globalised, causing devastating loss of biodiversity:
- WWF and RSPB’s 2020 Riskier Business report revealed that between 2016 and 2018 the UK used an overseas area 88% of its own size to supply our annual demand for just seven agricultural and forest products: soy, palm oil, timber, beef and leather, pulp and paper, rubber, and cocoa. That’s an overseas land footprint of 21.3 million hectares – a 15% increase from 2011-2015, showing that the harmful impact is growing.
- Commodity production causes over a quarter of global forest losshttps://science.sciencemag.org/content/361/6407/1108?ijkey=ed814495dc4905d212ca0117826aac01c7b2af3f&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha and is a major driver of biodiversity declinehttps://www.pnas.org/content/116/46/23202?ijkey=718e889664a736a342302141edcf26dcbbc57b66&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha. The IPBES (Intergovernmental Panel on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services) found that globally, 50% of agricultural expansion has occurred at the expense of forests.
- Soy production is the second largest driver of habitat loss in Brazil’s Amazon and Cerrado (tropical savannah) and Argentina and Paraguay’s Gran Chaco forest, behind beef. (Although the UK imports a small amount of Brazilian beef, even this has been linked to illegal deforestation). Around three-quarters of soy becomes livestock feed for chickens, pigs, farmed fish, and cows.
The damage from our industrialised agricultural system can no longer be ignored. Heavyweights in the field, from UNEP, the IPBES (biodiversity equivalent of the IPCC), Chatham House and even the World Economic Forum, agree that the rush for resources to fuel unsustainable consumption is driving environmental and social harm. The IPBES has said:
"The great expansion in the production of food, feed, fibre and bioenergy has occurred at the cost of many other contributions of nature to quality of life, including regulation of air and water quality, climate regulation and habitat provision. Synergies also exist, such as sustainable agricultural practices that enhance soil quality, thereby improving productivity and other ecosystem functions and services, such as carbon sequestration and water quality regulation”.
From IPBES Summary for policymakershttps://ipbes.net/sites/default/files/2020-02/ipbes_global_assessment_report_summary_for_policymakers_en.pdf.
Commodity demand worsens climate impacts
The fragmentation and loss of habitat from land clearance for commodities is a major contributor to the climate emergency:
- Deforestation, agriculture and other land use are responsible for almost a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissionshttps://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2019/08/4.-SPM_Approved_Microsite_FINAL.pdf.
- A large proportion of deforestation emissions (29-39%) comes from international trade in commodities, mainly beef, soy and palm oilhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959378018314365.
- Between 2011 and 2018, conversion of natural ecosystems and changes in land cover to produce just 4 of the commodities imported to the UK (soy, palm oil, cocoa, and rubber) led to average annual emissions of 28 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent. That is 7.7% of the UK’s entire overseas carbon footprint in 2016https://www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2020-07/RiskierBusinessSummaryReport_July2020_revised.pdf.
Demand puts communities under threat
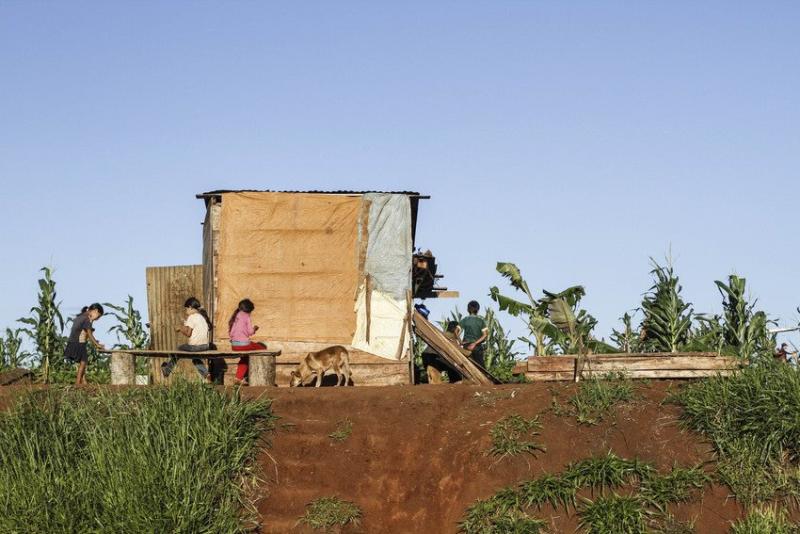
Everyone will be affected by the climate crisis and nature’s decline especially those who are least able to fend for themselves. The poorest people, like the Guarani communities in Paraguay, are already experiencing the effects of eroded ecosystems and climate breakdown.
Struggles over land rights linked to soy production, cattle ranching and logging, perpetuated by agribusiness, are particularly common in South America, but also occur linked to palm oil in Asia and Africa, leading to violent clashes, and even murder of environmental defenders.
- 2020 was the worst year on record for violent attacks on environmental defenders, with 227 people killed – all but one in the Global South.
- Women are often particularly affected, both by discrimination and labour abuses as well as loss of land, housing and access to food caused by land grabbing and resource degradation perpetuated by companies.
- Where communities are not immediately forced off their land or subjected to violence, they can still feel the harmful impacts of intensive agriculture. For example, excessive herbicide spraying of GM soy crops, leading to health impacts and pollution of water supplies (along with further harm to biodiversity) is common in Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay.
“Many companies engage in an extractive economic model that overwhelmingly prioritises profit over human rights and the environment. This unaccountable corporate power is the underlying force that has not only driven the climate crisis to the brink, but which has continued to perpetuate the killing of defenders.”
Last Line of defence report – Global Witness, 2021
How to reduce the impact of consumption
Halting deforestation and other habitat loss needs a wide range of measures and actors, including strong legal measures in producer countries - pledges such as those at COP26 but backed up by clear targets and robustly enforced. But alongside this, it's critical to address the ultimate drivers of this deforestation – our consumption of commodities and the role of agribusiness.
Changing how we consume
Firstly, we have to change our consumption patterns – what we eat, where it comes from and how it’s produced. In developed countries, we’re going to have to eat less meat and dairy and rely much less on imported animal feed.
Friends of the Earth is working with organisations as part of the Eating Better alliance to achieve a 50% reduction in meat and dairy eaten and produced in the UK – and for the rest to be produced to higher environmental and animal welfare standards, including use of home-grown feeds. This would go some way to reducing our global impact.
Regulating supply chains
Secondly, we must regulate the supply chains that control so much of our food, animal feed and fuel. Political opportunities to secure legal requirements for due diligence in supply chains are now opening up, in the UK, EU and elsewhere, as governments slowly start to respond to pressure to ensure that companies’ operations do not contribute to global biodiversity loss, the climate emergency and to human rights abuses.
Will the Environment Act help?
The new Environment Act contains provisions to address deforestation from the UK’s consumption of "forest risk commodities" like soy, beef, palm oil, cocoa, coffee and rubber. The use of products linked to illegal deforestation by some UK companies is prohibited and there is a requirement for those businesses to conduct due diligence to ensure their supply chains are free of products that come from illegally deforested areas.
This is a useful start but it doesn’t go nearly far enough and its weaknesses are widely acknowledged. It applies only to "illegal" deforestation as defined by producer country laws, many of which are weak and not properly enforced. It does not apply to the finance sector and human rights are not considered, so communities that face harm because of corporations’ activities may not be protected.
Legal deforestation is still causing huge harm, illustrated by a WWF report which estimates that 2.1 million hectares of Brazilian rainforest are vulnerable to encroachment by the soy sector alone under Brazilian law, and therefore not subject to the "illegal deforestation” requirement in the UK Act.
There is now further consultation over the secondary legislation that is needed to enact the provisions in the Environment Act, and it's critical to ensure it's implemented in the strongest possible way, including requiring that all commodities are included from the start.There is a suggestion in the consultation that the law would start with a small number of commodities and expand to the others over time.
Another new UK law to protect nature and people
To build on the Environment Act we need a new legal framework to ensure that the companies in the supply chains serving and fuelling our consumption aren’t destroying forests and other habitats, legally or illegally, and are respecting and protecting communities’ human rights.
Friends of the Earth is supporting the Corporate Justice Coalition campaign for a new Business, Human Rights and the Environment Act. This law would require companies to conduct human rights and environmental due diligence in order to identify and manage the risks that their activities pose - across their operations, subsidiaries and value chains – in the UK and globally.
The proposed new law would hold UK companies accountable if they fail to prevent harmful human rights or environmental impacts. It would mean that companies could not hide behind the excuse that they have long and complex supply chains. They would need to have more than paper-based standards and do proper checks. The law would include deterrent sanctions, liability provisions and enable access to justice for victims. It would cover companies in all sectors and of all sizes, and include the finance sector, public sector bodies, government departments, local authorities, development finance agencies and UK Export Finance. It could be a game-changer.
Businesses and public on board
Rather than pushing back on this idea, 36 leading businesses including Unilever, Nestlé and Tesco have signed a statement calling for mandatory environmental and human rights due diligence requirements:
“Legislation can contribute to a competitive level playing field, increase legal certainty about the standards expected from companies, ensure consequences when responsibilities are not met, promote engagement and impactful actions between supply chain partners and, above all, incentivise impactful and effective action on the ground.”
UK public opinion is strongly in favour as well, with recent YouGov polling showing high levels of support for a new UK law.
The EU has also tabled a new corporate due diligence directive for consultation. This will apply to all companies operating in the single market, including UK businesses, regardless of whether a trade agreement is in place. Failure on the part of the UK to keep step with the EU on this issue would put UK business at a competitive disadvantage.
The government needs to catch up (again)
It’s becoming a bit of a broken record. The government is way behind businesses and society – whether in it’s its pig-headed support for net zero-derailing projects like funding for a gas pipeline in Mozambique at the expense of local communities or failure to grasp the nettle and encourage and enable people to access healthy, sustainable diets with less and better meat.
On the need for a new UK due diligence law, these businesses, while far from perfect, have shown once again they are way ahead of the government, recognising the broader value to society and the potential for the UK to show leadership as part of its Global Britain agenda.
Deforestation continues
With the clock ticking on the climate and biodiversity crises, a plethora of campaigns and initiatives have sought to halt deforestation, clean up commodity supply chains, and address the environmental and health impacts of excessive meat consumption.
The latest of these came at COP26, the international climate talks, in Glasgow in November. For the first time in such a high profile climate space, nature was firmly on the agenda, with leaders of over 120 countries supporting a headline-catching pledge to halt deforestation by 2030. But to date, voluntary initiatives have failed to slow the climate and nature crises and their knock-on impacts on communities. Deforestation marches on at an alarming rate: from 2001 to 2020, there was a 10% decline in global tree cover, and the 2020 assessment report of the NYDF (New York State department of Financial Services) found that “Annual CO2 emissions from tropical forest loss are equal to the total emissions of the European Union”.
The Climate Conference in Glasgow may have ended but the issues remain firmly on the table. The UK holds the COP presidency until November 2022, giving it a key role in leading international action. The upcoming biodiversity COP to be hosted by China later in 2022 is also a critical moment to make progress
Thirteen years on from my visit to Paraguay and I’m not giving up. Friends of the Earth is working with many other organisations to campaign for a new UK Business, Human Rights and Environment Act, and to ensure the Environment Act is robustly implemented.
The best way for the UK to realise its pledge to be a global leader on nature and climate is by taking bold and urgent action at home.
It’s time for the government to walk the talk.